What is a CDN
What is a CDN
What is a CDN?
A content delivery network (CDN) refers to a network of servers strategically placed in various locations worldwide. Its primary function is to store and distribute content in close proximity to end users. By caching HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, videos, and other assets necessary for loading Internet content, CDNs enable swift content delivery.
CDNs have witnessed a remarkable surge in popularity, with the majority of web traffic now being served through them. Prominent websites like Facebook, Netflix, and Amazon rely on CDNs to efficiently handle their traffic. Moreover, a well-configured CDN can also act as a defense against common malicious attacks, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, providing an added layer of protection for websites.
Is a CDN the same as a web host?
Although a CDN cannot serve as a content host or replace the necessity for appropriate web hosting, it plays a vital role in caching content at the network edge, thereby enhancing website performance. Numerous websites encounter difficulties in meeting their performance requirements with conventional hosting services, prompting them to choose CDNs instead.
CDNs are widely preferred due to their ability to minimize hosting bandwidth through caching, prevent service interruptions, and enhance security. By alleviating some of the significant challenges associated with traditional web hosting, CDNs have become a popular choice.
What are the benefits of using a CDN?
While the advantages of utilizing a CDN may vary based on the size and requirements of an internet property, they can generally be categorized into four distinct components:
Enhanced website load times: By leveraging a nearby CDN server and implementing various optimizations, content can be distributed closer to website visitors. This results in faster page loading times, reducing bounce rates and encouraging visitors to spend more time on the site. In essence, a faster website translates to increased visitor retention and engagement.
Reduced bandwidth costs: Bandwidth consumption expenses for website hosting are a significant cost factor. CDNs employ caching and other optimization techniques to decrease the amount of data that needs to be provided by the origin server. Consequently, hosting costs for website owners are reduced.
Improved content availability and redundancy: Traffic surges or hardware failures can disrupt the normal functioning of a website. Due to their distributed nature, CDNs are capable of handling high volumes of traffic and are more resilient against hardware failures compared to individual origin servers. This ensures continuous availability of content and improves overall website reliability.
Enhanced website security: CDNs contribute to bolstering website security through various means, including DDoS mitigation, improved security certificates, and other optimization measures. By incorporating these security features, CDNs help safeguard websites against malicious attacks and enhance overall protection.
In summary, CDNs offer benefits such as faster website loading times, reduced bandwidth costs, improved content availability, and enhanced website security. These advantages make CDNs an attractive choice for website owners, irrespective of their website’s size and requirements.
How does a CDN work?
A CDN, at its essence, is a network of interconnected servers designed to efficiently deliver content with speed, cost-effectiveness, reliability, and security in mind. To ensure faster connectivity, CDNs strategically position servers at exchange points where different networks intersect.
These exchange points, known as Internet exchange points (IXPs), serve as central locations where various internet service providers connect with one another to facilitate the exchange of traffic generated on their respective networks. By establishing connections at these high-speed and extensively interconnected locations, CDN providers can minimize costs and transit times associated with delivering data at high speeds.
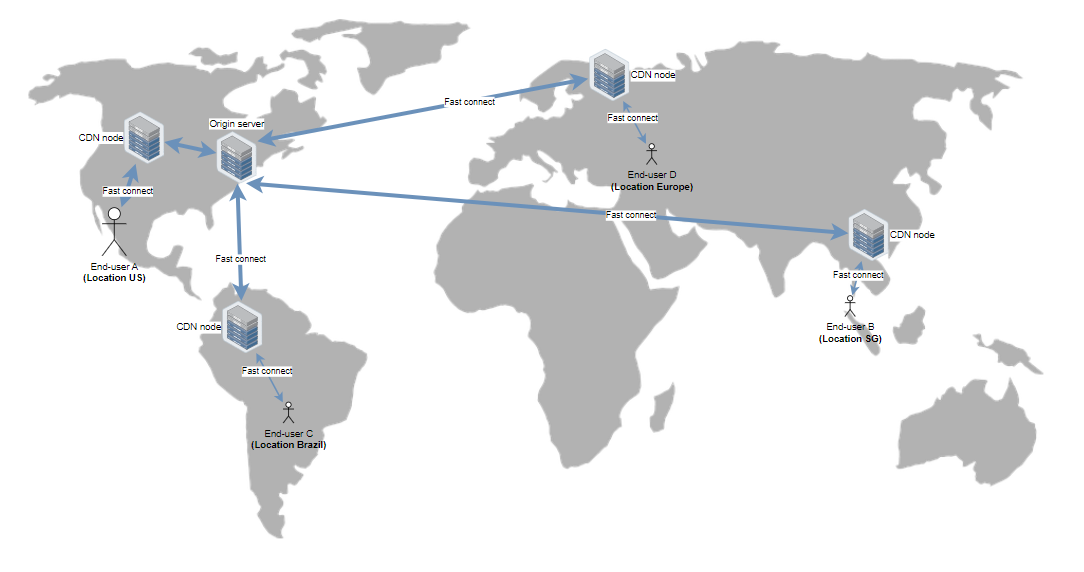
In addition to server placement at IXPs, CDNs employ several optimizations to enhance standard client/server data transfers. They strategically position data centers in key locations worldwide, bolster security measures, and employ designs that can withstand various types of failures and internet congestion. This comprehensive approach ensures efficient content delivery across the globe.
-
Latency - How does a CDN improve website load times? Websites lose users quickly if they load content slowly. CDN services offer various methods to reduce load times:
-
Minimizing Distance: CDNs have a distributed network across the globe, bringing website resources closer to users. Instead of connecting to a website’s origin server, users can connect to a nearby data center. This reduces travel time and improves service speed.
-
Optimizing Hardware and Software: CDNs employ hardware and software optimizations like efficient load balancing and solid-state hard drives. These enhancements enable faster data delivery to users, improving overall performance.
-
Data Reduction: CDNs reduce data transfer by employing tactics like minification and file compression. They decrease file sizes, resulting in faster load times. By sending smaller files, CDNs enhance the efficiency of content delivery.
-
TLS/SSL Optimization: CDNs can accelerate websites that utilize TLS/SSL certificates by optimizing connection reuse and enabling TLS false start. These optimizations help establish secure connections more quickly, further enhancing site speed.
Explore all the ways a CDN helps websites load faster
-
Reliability and redundancy - How does a CDN keep a website always online? Ensuring continuous uptime is crucial for individuals or organizations with an online presence. The occurrence of hardware failures or sudden increases in web traffic, whether caused by malicious attacks or a surge in popularity, can potentially lead to a web server going offline and preventing users from accessing a website or service. A comprehensive content delivery network (CDN) incorporates several features that effectively reduce the occurrence of downtime:
-
Load balancing: By evenly distributing network traffic across multiple servers, load balancing simplifies the process of scaling up to handle sudden spikes in traffic efficiently.
-
Intelligent failover: In the event that one or more CDN servers experience hardware malfunctions and go offline, intelligent failover ensures uninterrupted service. It redistributes the traffic to other operational servers, guaranteeing seamless accessibility.
-
Anycast routing: If technical difficulties affect an entire data center, Anycast routing swiftly transfers the traffic to an alternative available data center. This mechanism guarantees that users do not lose access to the website even during data center issues.
To delve deeper into how a CDN contributes to maintaining website availability, learn more about its functionalities.
Data security - How does a CDN protect data?
CDNs play a crucial role in maintaining information security. They offer a reliable means to secure websites by providing up-to-date TLS/SSL certificates, thereby ensuring a robust level of authentication, encryption, and data integrity. It is important to delve into the security considerations associated with CDNs and explore effective measures for securely delivering content. Let’s delve into the realm of CDN SSL/TLS security to gain a comprehensive understanding.
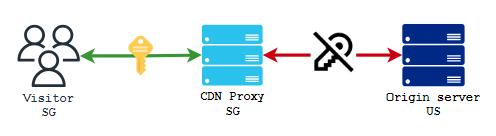
Bandwidth expense - How does a CDN reduce bandwidth costs?
Each request to an origin server consumes bandwidth whenever it responds. Discover how a CDN such as TOFFS minimizes origin requests and lowers expenses related to bandwidth usage.
